
What Is CNC Machining? Five Most Common CNC Machines
CNC machines revolutionised the machining industry when first introduced in the mid-20th century. Numerical control allowed for more precise operations and greater consistency in the manufacturing process. Today, CNC machining is a staple in the machining industry, and the machines have become more capable than ever.
The world of CNC machining is constantly evolving, and new machines are being introduced all the time. The most common machines used nowadays include CNC routers, CNC lathes, CNC mills, CNC lasers, and CNC plasma cutters. They all have their own characteristics that make them suitable for different applications.
CNC machines offer a lot of versatility and can be used for a wide range of machining operations. Below, you will find brief descriptions of each machine, as well as some of the most common applications.
Read on to learn more about CNC machining and the different machines available…
What is CNC Machining?
In general, the term CNC machining refers to any machining operation that is controlled by a computer. This can include anything from simple drilling and milling operations to more complex operations such as 3D printing and laser cutting. CNC machines are used in a variety of industries, including automotive, aerospace, and electronics.
CNC machining allows for a lot of flexibility in the manufacturing process thanks to the wide variety of tools that can operate on the same principles, ranging from a 4×8’ CNC router you can install in your workshop to large-scale industrial machines. The precision, efficiency, and repeatability of CNC machining make it an essential technology in modern manufacturing.
Common CNC Machines
CNC machines come in all shapes and sizes, but they can be broadly classified according to their main characteristics.
The most common types of CNC machines are:
CNC Lathes
CNC lathes, also known as turning machines, are probably the most common type of CNC machine. They are used to create cylindrical parts by cutting and shaping materials such as metals, plastics, and composites, on a rotating lathe. CNC lathes can be either horizontal or vertical, and they can be equipped with a variety of tooling options to suit different applications.
Lathes can also be used to drill and boreholes, create threading and add other features to parts. The chisels, cutting tools, and other tooling options can be replaced in most machines, allowing for one machine to be used for a variety of different operations.
CNC Mills
CNC milling machines are used to create parts with flat surfaces by cutting materials on a still or rotating milling table. In contrast to CNC lathes, which create parts by cutting them on a rotating lathe, CNC mills use cutting tools that move in two or more axes to create the desired shape.
Mills can be equipped with a variety of tooling options, including end mills, ball mills, and face mills. Again, the type of tooling used will depend on the machined material and the desired finish. CNC mills are available in both horizontal and vertical configurations, and they can be either floor-standing or benchtop models.
CNC Laser Machines
These can be considered a subtype of CNC mills, with the major difference being that they use a laser beam to cut materials instead of cutting tools. This allows for greater precision when cutting delicate materials, and it also eliminates the need for sharpening or replacing cutting tools.
More complex laser machines can be used to engrave, remove rust, or even weld. The laser beam’s depth, width, and power can be controlled to create different effects on the material. However, not all materials can be cut with a laser beam – with glass being a rather obvious example – and the energy efficiency of laser machines can be an issue in some applications.
CNC Routers
CNC routers are similar to CNC mills, but while they are generally quicker and have a higher cutting speed, they are not as precise. Routers can be used to cut a variety of soft materials like composites, wood, and plastic. The shapes that can be cut are only limited by the size of the router bit and the speed and power of the router.
The main benefit of using a CNC router over a more traditional cutting method is the fact that the cutting process is computer-controlled. This allows for greater consistency and repeatability that, along with greater efficiency, make CNC routers a popular choice for many woodworking and construction applications.
CNC Plasma Cutter
CNC plasma cutters use a plasma torch to cut materials, much like oxy-fuel cutting. It operates by blowing very hot gas through the cutting nozzle, creating an arc that vaporises the cut material. The plasma is then blown away by a stream of air, leaving a clean cut.
It is important to note that due to the nature of the process, CNC plasma cutters can only be used to cut electrically conductive materials, such as most metals. The cutting process is, however, much quicker than other methods, and it can be used to cut thicker materials.
Benefits of CNC Machining
As mentioned above, CNC machining is both more precise and effective than traditional machining methods – as long as the appropriate machine is selected for the application. CNC machines can be used to create parts with tight tolerances, and the repeatability of the process ensures that each part is identical to the last.
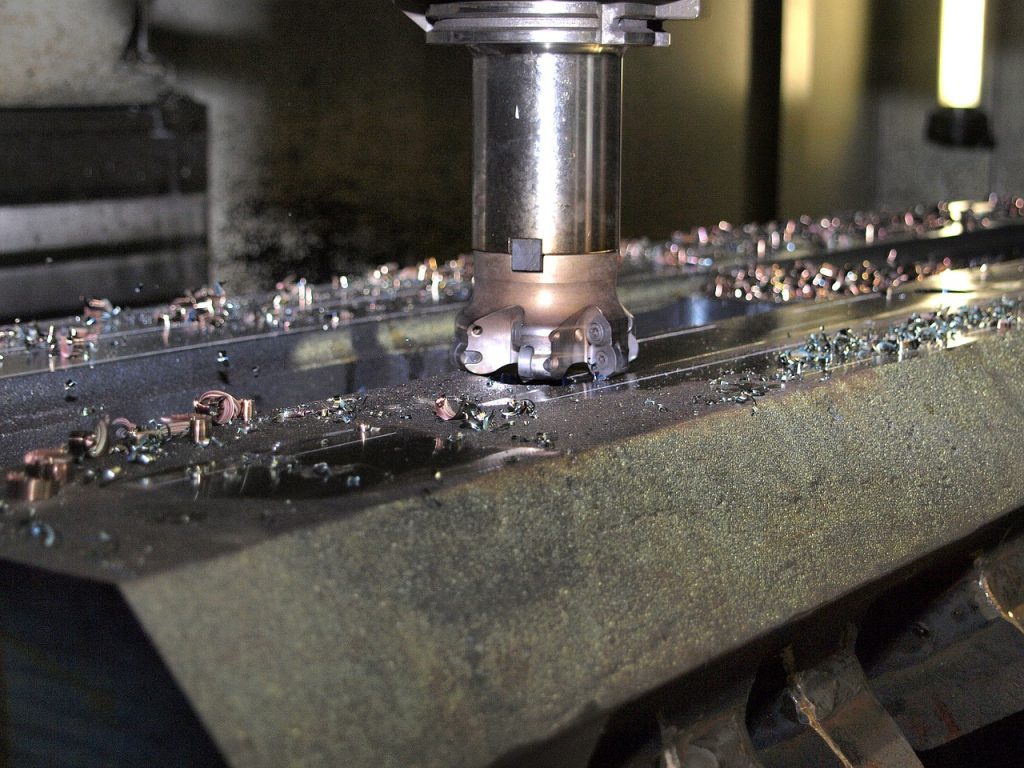
Laser or plasma cutters also offer a cleaner cut than traditional methods, and the lack of physical contact between the cutting tool and the material being cut eliminates the risk of damage to delicate parts. Furthermore, such cuts leave close to no burrs or other imperfections that would need to be removed in post-processing.
Final Thoughts
The benefits of CNC machining are numerous, and the technology has revolutionized the manufacturing industry. CNC machines offer a lot of versatility, and the most common ones – CNC lathes, mills, routers, and laser and plasma cutters – can be used for a wide range of applications.
When choosing a CNC machine, it is vital to consider the material you will work on and the desired finish. Different machines are better suited for different applications, and the wrong machine can lead to subpar results. So, make sure to do your research before picking one for your next project.
Latest news

15th April 2025
West Fraser: CaberDek earns top marks from Home Counties carpentry specialist
A specialist carpentry sub-contractor covering housing sites across a large swathe of the Home Counties has come to value CaberDek from the West Fraser range for a variety of reasons: not least because the high quality panel product doesn’t destroy his operatives’ electric saws!
Posted in Articles, Building Industry News, Building Products & Structures, Building Systems, Case Studies, Restoration & Refurbishment, Retrofit & Renovation, Roofs, Timber Buildings and Timber Products, Wooden products
15th April 2025
GEZE: The Role of Access Control Systems in Enhancing Building Safety
Jane Elvins, Specification and Business Development Manager at GEZE UK, delves into the role of access control systems in enhancing building safety…
Posted in Access Control & Door Entry Systems, Architectural Ironmongery, Articles, Building Industry News, Building Products & Structures, Building Services, Doors, Facility Management & Building Services, Health & Safety, Restoration & Refurbishment, Retrofit & Renovation, Security and Fire Protection
11th April 2025
Don’t Do a Dave! It’s Time to Lock FIT Show 2025 in Your Calendar!
It’s that time again – FIT Show is back! You could be forgiven for thinking there won’t be much new to see when FIT Show returns to the NEC from 29 April – 1 May. Wrong!
Posted in Articles, Building Industry Events, Building Industry News, Building Products & Structures, Building Services, Continuing Professional Development (CPD's), Exhibitions and Conferences, Information Technology, Innovations & New Products, Restoration & Refurbishment, Retrofit & Renovation, Seminars, Training
11th April 2025
Insight Data: Boost construction success with project and prospect data
For those working in construction – in whatever capacity – the last few years haven’t been much fun. And according to the latest statistics, it would seem the challenges are continuing – Alex Tremlett, Insight Data’s Commercial Director, has more…
Posted in Articles, Building Industry News, Building Services, Information Technology, news, Research & Materials Testing
 Sign up:
Sign up: