Sustainable heating system for the industrial and commercial market
With climate change an increasing concern, we are using renewable energy sources, such as the sun and the wind, to heat our buildings.
Unfortunately, many renewable technologies are unsuitable for the large steel clad structures which are used for diverse buildings, such as leisure centres, factories and retail outlets.
Sustainable living can also come at a high price, which causes further problems for the occupants of these buildings.
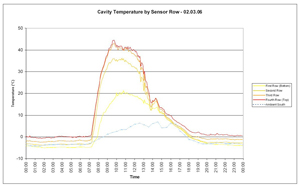
A typical heat gain graph from SolarWall
SolarWall: a sustainable heating solution
SolarWall is a sustainable heating system that works without turbines, heat pumps or photo-voltaic cells.
Taking the form of steel cladding, the product has been designed to capture the sun’s warmth.
It uses solar heated air to heat the building.
Also available in aluminium, the cladding is suitable for industrial and commercial buildings.
It is an ecological alternative to traditional renewable energy technologies.
On a clear, sunny day, SolarWall is able to generate enough heat to warm an entire building whilst on cloudy days, it relies on pre-heated air.
Fitted to the southern exterior elevations of a building’s envelope, it also provides solar shading in the summer, reducing the need for additional ventilation and cooling.
Offering reduced energy bills, the SolarWall can improve air quality and distribution in a building.
How SolarWall works
How does it work?
The cladding is manufactured from aluminium or ColourCoat pre-coated steel from Corus.
Each panel comprises around 2,500 small perforations per square metre.
Solar heated air is drawn through these perforations and then fed into the air cavity.
From here, it is introduced into a heating system and distributed throughout the building.
The warmed air can then recover hot air that has risen to the ceiling and would otherwise be wasted.
SolarWall can be used in conjunction with a fully integrated AmbiRad heating system.
In the case of a retro fit installation, where existing heating systems are already fitted, a fan can be used to distribute the warmed air instead.
Savings with SolarWall
To test SolarWall, the CA Group installed a system on one of its existing buildings.
A thermographic survey and an air permeability test were carried out; 16 temperature and humidity sensors were also fitted to monitor heat distribution and stratification levels.
Following the installation, the building was noticeably warmer and heat was distributed more evenly throughout.
Twelve months after SolarWall was fitted, the CA Group reported a 50% saving of its fuel costs for heating.
SolarWall and AmbiRad: an integrated heating solution
AmbiRad’s gas-fired heating system can be connected to SolarWall and its distribution duct
The company also used SolarWall cladding on a new development.
It was installed to heat its extended production facility in Evenwood, working with three gas-fired warm air heating units from AmbiRad.
When used in conjunction with AmbiRad’s heating systems, the SolarWall is able to effectively harness solar energy and meet a building’s heating requirements.
Controlled by a single system, the integrated heating solution offers energy savings to buildings that are incompatible with other sustainable technologies.
Contact:
Nortek Global HVAC UK,
Fens Pool Avenue,
Brierely Hill,
West Midlands,
United Kingdom,
DY5 1QA
Visit Supplier's page
Latest news

11th April 2025
Don’t Do a Dave! It’s Time to Lock FIT Show 2025 in Your Calendar!
It’s that time again – FIT Show is back! You could be forgiven for thinking there won’t be much new to see when FIT Show returns to the NEC from 29 April – 1 May. Wrong!
Posted in Articles, Building Industry Events, Building Industry News, Building Products & Structures, Building Services, Continuing Professional Development (CPD's), Exhibitions and Conferences, Information Technology, Innovations & New Products, Restoration & Refurbishment, Retrofit & Renovation, Seminars, Training
11th April 2025
Insight Data: Boost construction success with project and prospect data
For those working in construction – in whatever capacity – the last few years haven’t been much fun. And according to the latest statistics, it would seem the challenges are continuing – Alex Tremlett, Insight Data’s Commercial Director, has more…
Posted in Articles, Building Industry News, Building Services, Information Technology, news, Research & Materials Testing
11th April 2025
ASSA ABLOY EMEIA: Learn how to tackle the security challenges of digitalising access with insights from industry experts
In a new series of videos, experts in various specialisms within ASSA ABLOY share their expertise on digital access, including the complexities to overcome and the range of benefits for those who get digital access right…
Posted in Access Control & Door Entry Systems, Architectural Ironmongery, Articles, Building Industry News, Building Products & Structures, Building Services, Doors, Facility Management & Building Services, Information Technology, Innovations & New Products, Posts, Restoration & Refurbishment, Retrofit & Renovation, Security and Fire Protection, Videos
10th April 2025
Geberit completes 150 Acts of Kindness
Geberit has raised nearly £14,000 for various charities through its ‘150 Acts of Kindness’ initiative, a year-long programme of fundraising and volunteering to mark the company’s 150th anniversary in 2024.
Posted in Articles, Bathrooms & Toilets, Bathrooms, Bedrooms & Washrooms, Building Industry Events, Building Industry News, Building Products & Structures, Building Services, Charity work, Drainage, Interiors, Pipes, Pipes & Fittings, Plumbing, Restoration & Refurbishment, Retrofit & Renovation
 Sign up:
Sign up: