Understanding thermal bridging
With a drive towards more energy efficient homes, thermal bridging is becoming more important within the industry. But what is thermal bridging?
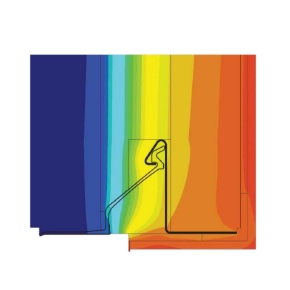
A thermal bridge is part of the building envelope through which heat is transferred at a substantially higher rate than through the surrounding area. The heat loss at these junctions are considered independently of the U-Values of the elements.
It has been found that up to 30% of all heat loss from buildings is due to thermal bridging. Therefore, building regulations now require the heat loss through U-Values and Thermal Bridging (Psi values) to be accounted via SAP calculations.
The two main types of thermal bridges in building are repeating and non-repeating. Repeating thermal bridges occur regularly within a typical dwelling; for example where timber studs bridge a layer of insulation in a cavity wall. These are taken into account in the ‘U-Value’ calculation.
Non-repeating thermal bridges occur at junctions between building elements and around openings, these are measured as Psi values (linear thermal heat transmittance). The Psi values are accounted for in the SAP calculation.
Non-repeat thermal bridging is measured as a Psi Value, which is a measure of linear thermal heat transmittance usually at a junction in a dwelling. A Psi value is calculated using specialist thermal modelling software, where the thermal modeller will draw the construction detail in the software package and add in the material conductivities. This sophisticated software then calculates the heat loss at the junction, subsequently producing a Psi value.
Psi values are based on standard construction details but default Psi values can be enhanced through the use of thermal modelling by a third party-accredited assessor. Improved Psi values can help eliminate the need for costly eco add-ons, such as solar panels, and are worth exploring as a means to reduce the cost of a new build whilst meeting fabric requirements, energy requirements of Part L of the building regulations and Code of sustainable homes.
Visit the Keystone Lintels website
Download the Keystone Lintels Product Guide
Download the Hi-therm+ brochure
Download the Keyslip Brick Feature Lintels brochure
Visit Supplier's page
Latest news

25th April 2025
Quicker and Easier Inspections with High Performance FLIR Testing Solutions
FLIR, a Teledyne Technologies company, introduces its PV range of inspection solutions to expedite panel installation and maintenance at solar farms, commercial buildings, and residential buildings.
Posted in Articles, Building Industry News, Building Products & Structures, Building Services, Facility Management & Building Services, Information Technology, Innovations & New Products, Research & Materials Testing, Restoration & Refurbishment, Retrofit & Renovation, Sustainability & Energy Efficiency, Thermal Imaging and Monitors
25th April 2025
Schlüter-Systems: Common costly mistakes when renovating a bathroom
With nearly six decades of experience in the bathroom world, Schlüter-Systems knows all there is to know about the challenges of installing a perfect one!
Posted in Articles, Bathrooms & Toilets, Bathrooms, Bedrooms & Washrooms, Building Industry News, Building Products & Structures, Building Services, Damp & Waterproofing, Drainage, Drainage Services, Drainage, Guttering, Soffits & Fascias, Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning - HVAC, Interior Design & Construction, Interiors, Membranes, Pipes & Fittings, Plumbing, Restoration & Refurbishment, Retrofit & Renovation, Walls
25th April 2025
Newcastle United enhances fans’ experience with Stannah escalators
Newcastle United Football Club has introduced two new Stannah escalators as part of a refurbishment of its on-site merchandising outlet.
Posted in Accessibility, Articles, Building Industry News, Building Products & Structures, Building Services, Case Studies, Facility Management & Building Services, Restoration & Refurbishment, Retrofit & Renovation
24th April 2025
Gemini: Using Data Loggers to Help Analyse Environmental Conditions and Energy Usage in Buildings
Gemini Tinytag Data Loggers record environmental parameters over time, allowing conditions to be measured, documented, analysed, and validated.
Posted in Articles, Building Industry News, Building Products & Structures, Building Services, Facility Management & Building Services, Health & Safety, Heating Systems, Controls and Management, Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning - HVAC, Information Technology, Research & Materials Testing, Restoration & Refurbishment, Retrofit & Renovation, Sustainability & Energy Efficiency, Thermal Imaging and Monitors
 Sign up:
Sign up: